Troubleshooting
Here are the most common problems encountered when installing and using Exegol.
Unable to connect to Docker
There are multiple checks to do to make sure Docker works properly.
The Docker service must installed up and running.
- For Windows users: Docker Desktop for Windows must be up and running.
- For macOS users: Docker Desktop for Mac (or OrbStack) must be up and running.
X11 on non-Linux hosts
X11, or X Window System, is a graphical windowing system that provides a framework for creating and managing graphical user interfaces (GUIs) in Unix-like operating systems.
X11 sharing between an Exegol container and a host allows a graphical application running within the container to display its GUI on the host's X11 server. This means you can run graphical applications in Exegol containers and have them appear as if they were running directly on the host machine. It enables the execution of GUI-based applications in isolated containers while interacting with them through the host's graphical interface.
For macOS users, XQuartz is needed. It's listed in the install requirements.
Exegol's wrapper automatically starts XQuartz on macOS hosts when needed. But if for some reason it gets manually closed by the users while a container is running, X11 sharing will not work. Restarting the container with exegol restart <container> will restart XQuartz automatically if needed.
Docker download errors
Rate limiting
When downloading Docker images, you may encounter rate limiting errors from Docker Hub. This happens when you exceed the anonymous pull rate limit, which is likely to occur if you're on a shared network where people pull lots of images from Docker Hub.
To resolve this, create a Docker Hub account and authenticate (docker login), and retry the failing command.
Time synchronization
Docker image downloads may be time-sensitive. In the case of dual-boot systems, it is common to experience time lags of a few hours.
To correct the problem, check that your computer's date and time are correct.
Disk space
Docker Desktop is a tool used for running Docker containers on Windows and macOS. However, it uses a virtual disk to store Docker images, containers, and volumes. The virtual disk used by Docker Desktop is not dynamic; it has a fixed size, which by default is set to 64GB.
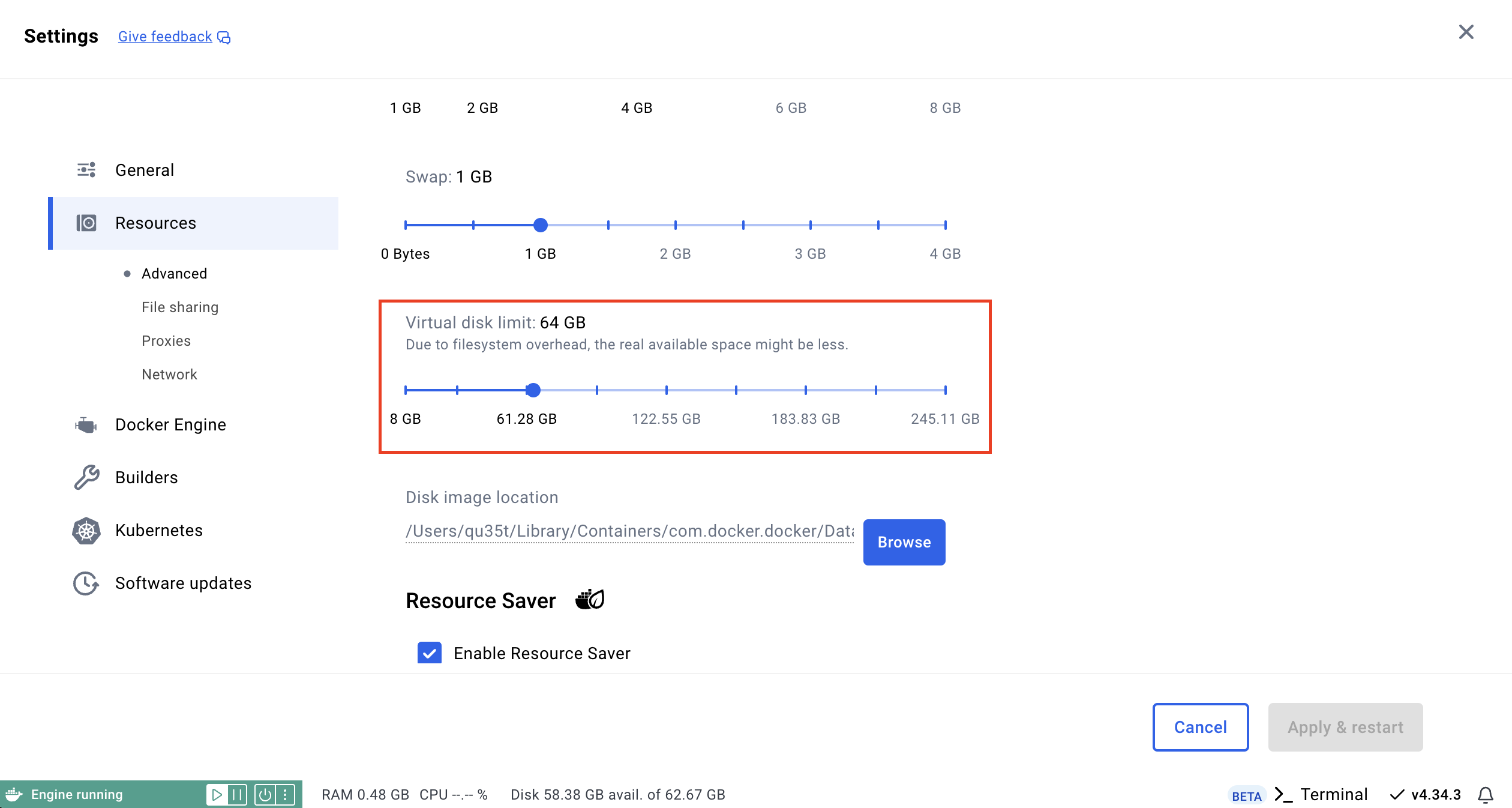
Exegol images can be quite large, with some reaching over 50GB. This can quickly exceed the available virtual disk space, even if your physical disk still has free space. To resolve this issue, you need to allocate more space to the Docker Desktop virtual disk.
To increase the virtual disk size, open Docker Desktop and go to Settings -> Resources -> Advanced. Locate the Virtual disk limit option and increase the allocated size. Make sure to choose a value that provides enough space for your images and containers, such as 128GB or more depending on your needs.
Apply the changes and then restart Docker Desktop to ensure the new configuration takes effect.
If you decide to reduce the size of the virtual disk, be aware that Docker Desktop will completely delete the virtual disk image. This action will remove all Docker images, containers, and volumes stored on the disk. Therefore, before reducing the disk size, make sure to back up any important data or export your Docker images to avoid data loss.
CRLF errors on Windows
If you have cloned the Exegol repository on Windows, you may encounter errors when launching your container, for example:
/.exegol/entrypoint.sh: line 3: trap: SIGTERM : invalid signal specification
/.exegol/entrypoint.sh: line 4: $'\r': command not found
/.exegol/entrypoint.sh: line 5: syntax error near unexpected token $'{\r''
/.exegol/entrypoint.sh: line 5: function exegol_init() {This is caused by the automatic addition of CRLF linefeed by Windows to ensure compatibility. To correct this problem, simply disable this feature on the Exegol repository and reload the file of the repository:
cd ./Exegol
git config core.autocrlf false
git rm -rf --cached .
git reset --hard HEADEnvironment externally managed
When installing exegol with python3 -m pip install exegol on modern operating systems (Ubuntu 23.04 and higher, Debian 12 and higher, macOS 14+), you may encounter the following error:
This environment is externally managed
To install Python packages system-wide, try apt install
python3-xyz, where xyz is the package you are trying to
install.
If you wish to install a non-Debian-packaged Python package,
create a virtual environment using python3 -m venv path/to/venv.
Then use path/to/venv/bin/python and path/to/venv/bin/pip. Make
sure you have python3-full installed.
If you wish to install a non-Debian packaged Python application,
it may be easiest to use pipx install xyz, which will manage a
virtual environment for you. Make sure you have pipx installed.
See /usr/share/doc/python3.11/README.venv for more information.
hint: See PEP 668 for the detailed specification.As the error message suggests, this error occurs when you try to install Python packages system-wide. To resolve this issue, you have two options :
Using pipx (Preferred)
The recommended way to install Exegol is using pipx, which automatically handles virtual environment creation:
pipx install exegolManual Virtual Environment
Alternatively, you can create and manage a virtual environment manually:
python3 -m venv path/to/venv
source path/to/venv/bin/activate
python3 -m pip install exegolTLS certificate verification issues
When using Exegol behind an enterprise proxy that performs TLS inspection, you may encounter certificate verification errors. This happens because the proxy's Certificate Authority (CA) is not automatically trusted by the system's truststore. This effectively prevents the wrapper from listing images (exegol info), activating a license, etc.
The error message raised by the wrapper may be: TLS certificate verification failed while contacting Exegol servers.
For detailed instructions on how to fix this issue, please refer to the Supabase discussions #29935 and #35590 which provide solutions for trusting the proxy's CA certificate.
A quick-fix may be to add the custom CA to Exegol's virtual env's certifi's CA bundle:
cat custom_ca.crt >> $(~/.local/pipx/venvs/exegol/bin/python -c "import certifi; print(certifi.where())")Make sure to trust the whole chain, if applicable
Arsenal TIOCSTI requirement
The arsenal tool needs the TIOCSTI functionality enabled. A GitHub issue exists to request an evolution: https://github.com/Orange-Cyberdefense/arsenal/issues/77.
This feature cannot be enabled only in exegol containers (docker limitation), it must be configured in the host with the following command:
# For the current session
sudo sysctl -w dev.tty.legacy_tiocsti=1
# Persistent configuration (as root)
echo "dev.tty.legacy_tiocsti=1" >> /etc/sysctl.confFor more information about installation, see the installation section.
Docker Breaks KVM Internet Access
When docker is installed alongside KVM/libvirt, Docker modifies iptables rules that conflict with libvirt’s virtual bridge (virbr0). This causes KVM virtual machines to lose internet connectivity. To restore connectivity in KVM, manually allow forwarding between KVM bridge (virbr0) and your physical interface
# Enable NAT for KVM VMs (virbr0 network) through your physical interface
sudo iptables -t nat -C POSTROUTING -s 192.168.80.0/24 -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE
sudo iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.80.0/24 -o eth0 -j MASQUERADE192.168.80.0/24 is the default subnet of the virbr0 bridge used by KVM/libvirt and eth0 is the network interface.
This ensures KVM virtual machines can access the internet even when Exegol is running.
Error When Mounting NFS
When attempting to mount an NFS share inside Exegol, you may encounter the following error:
mount.nfs: rpc.statd is not running but is required for remote locking.
mount.nfs: Either use '-o nolock' to keep locks local, or start statd.
mount.nfs: Operation not permittedThis occurs because the NFS mount operation requires rpc.statd for file locking, and the container lacks the necessary privileges and services to support this by default. To resolve this, run Exegol with --cap SYS_ADMIN, which grants the container the privilege needed for NFS and rpc.statd support.

